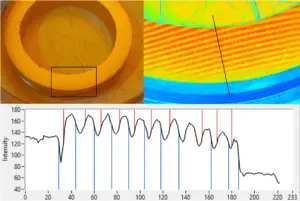
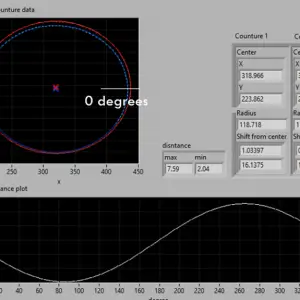
Interferometers are crucial tools in metrology for measuring the flatness of surfaces with high precision. Here’s a breakdown of the physics fundamentals behind interferometer measurements and their application in flatness interferometer testers:
Physics Fundamentals:
1. Wavefront Division: Interferometers work on the principle of dividing a wavefront of coherent light, usually from a laser, into two or more parts.
2. Coherence: The light used must be coherent, with all waves in phase, to produce clear interference patterns. Lasers provide the necessary spatial and temporal coherence.
3. Path Difference: When the divided light waves travel different paths and then recombine, their path difference will determine the type of interference (constructive or destructive) observed.
4. Constructive and Destructive Interference: If the path lengths are the same or differ by multiples of the wavelength, constructive interference occurs, creating bright fringes. If they differ by half a wavelength, destructive interference occurs, resulting in dark fringes.
5. Interference Patterns: The patterns of light and dark fringes, known as interferograms, are used to calculate the flatness of the surface being tested. Any deviation in flatness will change the path length of one of the beams, altering the interference pattern.
6. Reference Surface: In flatness measurement, one of the paths typically reflects off a reference surface known for its high degree of flatness, while the other reflects off the test surface.
Flatness Interferometer Tester:
Setup: A flatness interferometer tester typically
includes a stable light source (like a He-Ne laser), a beam splitter, a
reference surface, a test surface,
and a camera or detector to capture the resulting interference pattern.
Fizeau Interferometer: One common type of flatness
interferometer is the Fizeau interferometer, where the test and reference
surfaces are placed close to each other, and the cavity between them is
illuminated by a collimated light source.
Analysis: The interferogram is analyzed, often by
software, to assess the flatness of the test surface.
Environmental Control: Since interferometry is highly
sensitive, environmental factors like temperature, vibration, and air currents
must be controlled to obtain accurate measurements.
Calibration: Interferometer testers must be
calibrated using surfaces with known flatness to ensure measurement accuracy.
Non-Contact Method: As a non-contact method,
interferometry avoids any potential surface damage or alteration during
measurement.
Interferometer testers for flatness measurement are pivotal
in precision engineering, semiconductor manufacturing, optics production, and
other fields requiring surfaces with tight flatness tolerances. Their ability
to provide precise, non-contact measurements makes them an indispensable tool
in modern metrology.
Interferometers
can vary in complexity and design, but they all rely on these fundamental
principles of optics. The detailed analysis of the interference patterns they
produce allows for measurements of length, changes in refractive index, surface
irregularities, and the shapes of optical surfaces with exceptional precision.
This makes interferometry a powerful tool in scientific research, manufacturing,
and metrology.
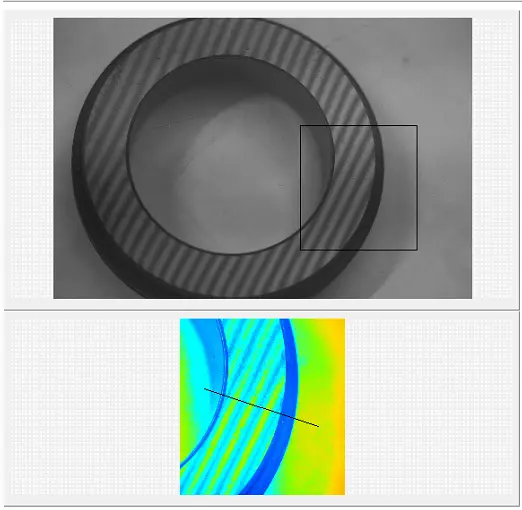
The importance of interferometer measurements for flatness can be distilled into several key points:
High Precision: Interferometers can measure flatness with extremely high precision, often up to fractions of a wavelength of light. This level of accuracy is essential for applications where surface flatness is critical, such as in the production of optical components, semiconductor wafers, and precision engineering surfaces.
Non-Contact Measurement: Interferometry is a non-contact measurement technique, which means that the testing process does not physically affect the surface being measured. This is crucial for delicate or finely finished surfaces where contact methods could cause damage or introduce measurement errors.
Speed and Efficiency: Interferometric measurements can be made quickly, which enables the inspection of large areas or multiple components in a relatively short time. This efficiency is vital in industrial settings where time and throughput are important factors.
High Resolution: Interferometers can resolve features at a nanometer scale, which is necessary for detecting and characterizing very small deviations in flatness that could significantly impact the performance of a component in a high-precision application.
Versatility: Interferometry can be used to measure flatness in various environments and on a wide range of materials. It is a versatile tool that can be applied to different phases of the manufacturing process, from initial production to final inspection.
Quality Control: For industries where the flatness of a product is a quality benchmark, such as in the manufacturing of lenses or mirrors, interferometry provides a reliable standard against which to verify product quality.
Data Analysis: Modern interferometers are often coupled with sophisticated software that can analyze and interpret data, providing comprehensive mapping of surface flatness and highlighting areas that require attention.
Standardization: Interferometric flatness measurements are standardized, allowing for consistent and repeatable results that are recognized internationally, which is beneficial for global industries and research.
At IZAK Scientific, we specialize in developing sophisticated software applications coupled with advanced image processing analysis for interferometer analysis. Our solutions are designed to facilitate precise quality assurance for parts requiring flatness testing. Our software not only performs thorough analysis but also generates detailed reports, ensuring that your production meets the highest standards of precision and quality.
We understand that each project has its unique requirements, and we are fully prepared to develop a customized interferometer analysis tool tailored to your specific needs. Whether it’s designing the software to fit within your existing system or creating a new solution from scratch, our team has the expertise to deliver high-quality results.
Additionally, if you need an interferometer specifically for flatness inspection, IZAK Scientific is here to assist. We can provide expert consultation to design an interferometer that perfectly aligns with your measurement needs, or we can deliver a complete, ready-to-use interferometer system. Our aim is to ensure that you have the best tools and knowledge at your disposal to conduct effective flatness inspections.
Let IZAK Scientific be your partner in achieving unparalleled accuracy and efficiency in your measurement processes. Contact us to discuss how we can assist in enhancing your quality assurance with our interferometer analysis tools and solutions.
Tzachi Sabati
CEO, IZAK Scientific
Physicist specializing in photonics and quantum technologies, with deep expertise in quantum sensors and advanced optical systems. Leads the Advanced Quantum Lab course at the Technion, bridging academic excellence with industry innovation. At IZAK Scientific, provides cutting-edge photonics-based solutions, developing customized inspection and sensing systems for R&D and production. Passionate about advancing quantum sensing applications and integrating novel technologies to meet industry needs.