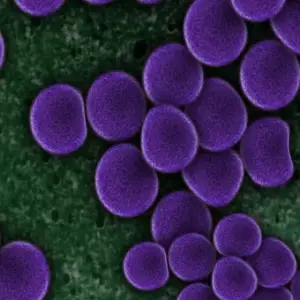
About MRSA
Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a strain of staph bacteria that is resistant to antibiotics. It was discovered in the 1960s in the hospitals, as patients were becoming infected, extremely ill, and dying. Later on is spread to nursing homes, then into the community, and now is found everywhere, worldwide.
How Did MRSA Develop?
MRSA is the result of overusing antibiotics. In an attempt to prevent infections, antibiotics had been increasingly prescribed. More patients with infections lead to more use of antibiotics which leads the staphylococcus to mutate and become resistant to antibiotics.
At this point, researchers believe that we are facing an MRSA epidemic, and the most affected countries include the US, Canada, Japan, and Indonesia.
MRSA is classified in three subtypes: HA-MRSA found in hospitals and nursing homes (healthcare-acquired), CA-MRSA is due to its spread in the community (community-acquired for example in gym facilities, daycare, schools) and LA-MRSA (livestock-acquired)- because antibiotics are used in food animals to treat diseases, to prevent and control common disease events, and to enhance animal growth.
Who Is At Risk To Get MRSA Infection?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO)- everyone is at risk to get this infection.
- Hospital patients- including those on dialysis, undergoing surgeries, or in intensive care units are at higher risk.
- Daycare, schools, gyms, and correction facilities are also affected by more exposure to these bacteria.
- Your pets (cats and dogs) and livestock – farm raises animals, as well as wildlife and zoo animals can also get infected.
How Deadly Is MRSA?
Many people carry this bacterium. They may not have any symptoms- but can infect others.
When bacteria enters the bloodstream- causing sepsis- it becomes very dangerous, with a mortality rate of 30-50%. About 119,000 bloodstream infections and nearly 20,000 deaths are attributable to staph infections in the US (2018 statistics). While healthy carriers can infect others, contaminated surfaces and medical equipment are also common ways to spread this infection. That’s why leading health authorities work hard to decontaminate surfaces to reduce the spread of MRSA- and save countless lives.
Will UV Light Sanitizer Kill MRSA?
We can’t comment on other UV devices, but we know that Fast PXL does kill MRSA. Really fast!
Hospitals, daycares, schools, gyms, and correction facilities can all benefit from using fast PXL to reduce the spread of MRSA.
We tested twice our PXL products. First, we use a third party independent lab to evaluate our device, which found that PXL Sanitizer is highly effective. There were 65 million MRSA cells on the surface and these cells started to die within seconds, when exposed to UVC light. At the end of the treatment, only a few bacterial cells remained on the surface.
More recently, we used high-quality UV dosimeters, which are safe and effective tools to verify UVC exposure, so you can really see if the device is doing its work.
The rule is very simple: The center of UVC dosimeter changes from yellow to orange to show that a level of energy deadly to MRSA has been delivered.
So we put the Fast PXL to the test.
Will UV light kill MRSA? Watch the video and see how fast and effective really is! In only 15 seconds!
Hospitals around the world trust UV light disinfectants such as pulsed xenon light to disinfect equipment and surfaces from MRSA. They also use UVC light to kill the novel coronavirus responsible for COVID-19.
Because UVC light does not discriminate- it kills MRSA, along with many other bacteria and viruses.
In regards to MRSA, Fast PXL could be a great additional disinfectant for daycare, schools, long term care homes, gyms, and correction facilities.
You need the IZAK Scientific team of experts to provide you training material and safety recommendations to get the UV light disinfectant that really works. Contact us today!
https://www.who.int/patientsafety/patients_for_patient/PFPS-webinar1_2013.pdf?ua=1
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12426452/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26014583/
Tzachi Sabati
CEO, IZAK Scientific
Physicist specializing in photonics and quantum technologies, with deep expertise in quantum sensors and advanced optical systems. Leads the Advanced Quantum Lab course at the Technion, bridging academic excellence with industry innovation. At IZAK Scientific, provides cutting-edge photonics-based solutions, developing customized inspection and sensing systems for R&D and production. Passionate about advancing quantum sensing applications and integrating novel technologies to meet industry needs.